Cybersecurity Analytics involves aggregating data for the purpose of collecting evidence, building timelines, and analyzing capabilities to perform and design a proactive cybersecurity strategy that detects, analyzes, and mitigates cyberthreats.
With a normal security information and event management (SIEM) system, you have to depend on testing things as they exist in a singular moment within the network. Cybersecurity analytics applies to the network as a whole, including general trends that may not be evident in a given snapshot.

What Is the Need for Cybersecurity Analytics?
A few reasons why cybersecurity analytics are needed:
Proactive rather than reactive cybersecurity. Several security systems will alert administrators to a data breach, but analytics monitor the environment for anomalies to alert administrators of suspicious activity before it becomes a data breach.
Complete views of network traffic. Cybersecurity analytics detect activity as it’s happening to give administrators a better view of network traffic.
Collection of data to show a return on investment for cybersecurity efforts. Every operational budget needs a return on investment to show that cybersecurity infrastructure is saving money on threat detection.
Benefits of Cybersecurity Analytics Tools
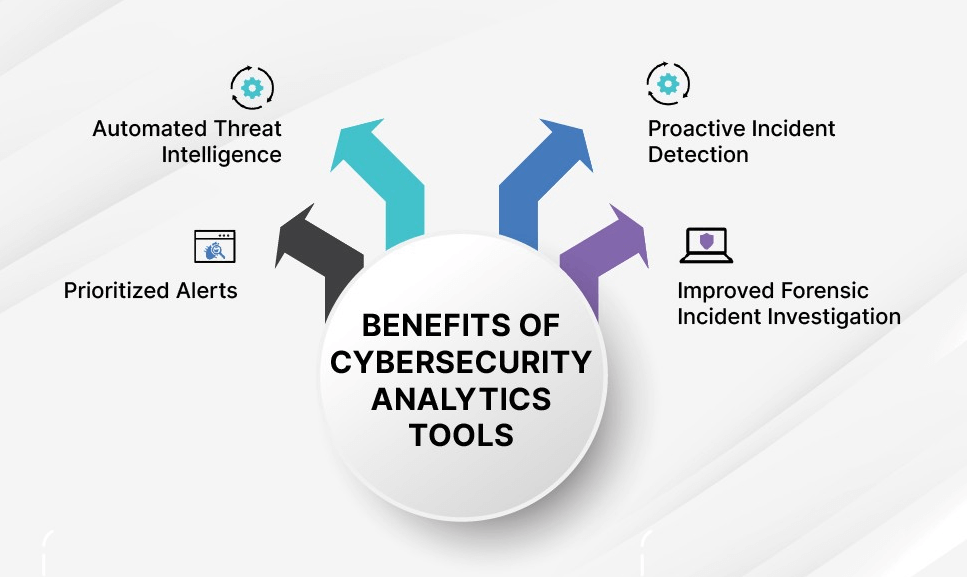
Prioritized alerts
Even though the vast number of cyber threats can result in your system being inundated with alerts, with cybersecurity analytics, you can prioritize the most pertinent alerts.
Automated threat intelligence
In some ways, cybersecurity analytics is like next-generation SIEM, particularly in how it automates your threat intelligence.
Proactive incident detection
A reactionary approach to cybersecurity can leave your system open to novel or developing threats. Cybersecurity provides you with a proactive strategy to identify and address threats, giving you a global view of not just what your network is currently dealing with but likely future threat events.
Improved forensic incident investigation
With security analytics, you can see where attacks come from, how they managed to get inside your system, and the assets they affected.
What Are the Different Types of Cybersecurity Analytics?
1. Behavioral Analytics
This type of analytics focuses on analyzing user behavior to identify potential threats. By monitoring user activities, such as login attempts, file access, and network traffic, security teams can detect unusual behavior that may indicate an attack.
2. Network Analytics
Network analytics involves analyzing network traffic to identify potential security threats. This includes identifying anomalies in traffic patterns, detecting unusual activity such as port scanning or unauthorized access attempts, and identifying potentially malicious connections.
3. Threat Intelligence Analytics
It involves analyzing external data sources, such as threat intelligence feeds, to identify potential security threats. By combining external data with internal security data, organizations can gain a more comprehensive view of their security posture and identify potential threats.
4. Cloud Security Analytics
It analyzes data generated by cloud-based applications and services to identify potential threats. This includes monitoring user activity in cloud environments, analyzing network traffic, and detecting potential threats such as unauthorized access attempts or data exfiltration.
5. Endpoint Analytics
Endpoint analytics focuses on analyzing data generated by endpoint devices, such as desktops, laptops, and mobile devices. This includes monitoring user activity, analyzing system logs, and detecting potential threats such as malware infections or unauthorized access attempts.
What are the challenges of Cyber Security Analytics?
Cybersecurity analytics, while promising, faces several significant challenges:
Data-Related Challenges
- Data Volume and Velocity: The sheer volume of data generated by networks and systems can be overwhelming. Real-time analysis of this data is crucial, but computationally intensive.
- Data Quality and Consistency: Inconsistent data formats, missing values, and noise can significantly impact the accuracy of analytical models.
- Data Privacy and Compliance: Handling sensitive data while adhering to regulations like GDPR and CCPA is complex and requires robust data protection measures.
Analytical Challenges
- Skill Gap: A shortage of skilled cybersecurity analysts with expertise in data science and machine learning hinders effective analysis.
- Model Development and Tuning: Creating accurate and reliable predictive models is challenging due to the evolving nature of threats.
- False Positives and Negatives: Balancing the detection of actual threats with minimizing false alarms is a constant challenge.
- Explainability: Understanding the reasoning behind model decisions is crucial for trust and accountability, but often difficult to achieve.
Organizational Challenges
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating cybersecurity analytics tools with existing security infrastructure can be complex and time-consuming.
- Change Management: Overcoming resistance to change and adopting new analytical approaches within the organization is often challenging.
- Resource Allocation: Securing adequate budget and personnel for cybersecurity analytics initiatives can be difficult.
Threat Landscape Challenges
- Evolving Threats: Cyber threats are constantly evolving, requiring continuous adaptation of analytical models.
- Advanced Persistent Threats : Detecting and responding to sophisticated, long-term attacks is particularly challenging.
- Insider Threats: Identifying malicious activities by authorized users is difficult due to the nature of their access privileges.
Addressing these challenges requires a combination of technological advancements, skilled personnel, and effective organizational strategies.
What are the Solutions for Cyber Security Analytics?
With Xenonstack Support, security analytics is divided into four sectors; users will predict attacks and prevent them before something serious.
Digital Security
- In digital security analytics, by using a dataset containing the historical data of the protocol used, type of attacks, source IP address, source port number, destination IP address, and destination port number, the entity can build, deploy, and refresh the models to predict incoming threats in real-time.
- Our prediction model allows analysts to monitor intrusion vectors and take action as soon as possible and protect the system from serious causes.
Data Security
- In Digital Security, One can protect the database, computer system, and websites from attack by doing analysis. For which CIA traits were violated, assets targeted penetration data and other information sources.
- Through this, an entity can find threats or attacks at an earlier stage and take action as early as possible.
Network Security
- In Cyber Security by Network Security analytics, one can build accurate and predictive models on real-time data to better understand the customer to get the information about their attacks, Vulnerabilities, events logs, and authentication user can bring clarity to the network connectivity.
- As a result, we have given the demo of the dashboards for user reference. You will be confident after getting the results for events logs, attack prediction results, etc. By seeing the dashboards, you will get information about how our machine-learning models work.
Communication Security
- In Communication Security analytics, one can build accurate and predictive models on real-time data. To better understand the customer to get the information about their communication of message delivery, encryption for TLS and Non-TLS between the networks.
- And here, the user will see the prediction on messages delivered through emails that are authenticated.
- As a result, we have given the demo of the dashboards for reference. You will be confident after getting the results for the encryption of messages, authentication, and spam filters using our machine-learning model. Users can easily get all the information about communication network security by applying our models.
Big Data Security Analytics
It is important to conform to governance regulations while ensuring your organization’s systems are secure and cyber risks are minimized. This requires processing loads of data—and quickly enough to make your findings actionable.
With big data security analytics, you can automatically collect information regarding all the endpoints on your network, as well as the behavior of individual users, groups of users, and subnetworks, including software-defined wide-area network (SD-WAN) connections. Big data analytics can also aggregate these large storehouses of data and analyze them to identify threats.
The Future of Cybersecurity Analytics
Although machine learning and artificial intelligence have been a component of cybersecurity analytics for years, platforms that use analytics tools are still in their infancy. The future of cybersecurity analytics requires more investigation into how threats are deployed and managed so that cybersecurity tools can be updated to deal with them.
Data and user behavioral patterns are critical factors in cybersecurity analytics, but attackers continue to change their own strategies to blend in with other users so that analytics tools cannot detect a data breach. As more users work from home, detecting threats is more difficult for administrators tasked with ensuring the continuity and security of the corporate environment.
Use Cases for Data Analytics in Cyber Security
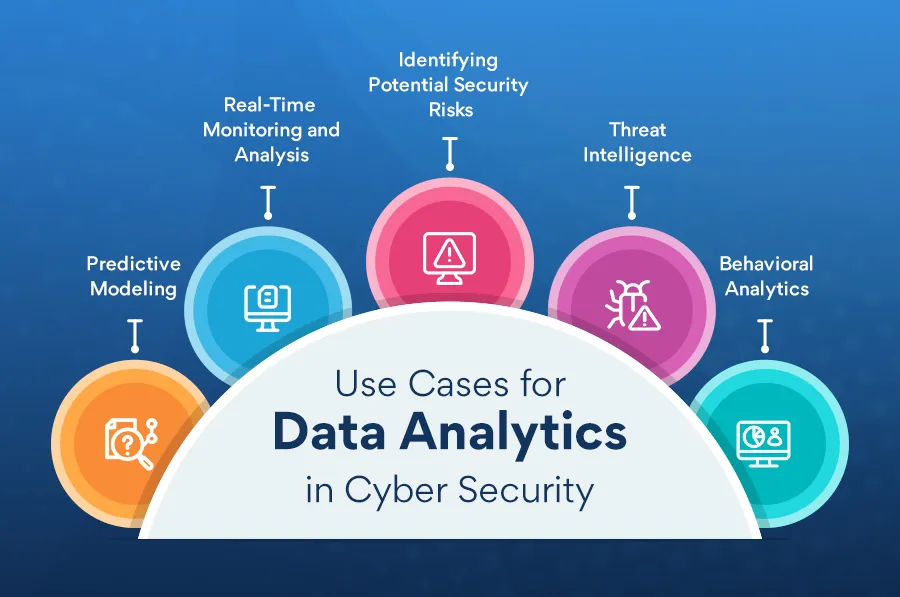
1. Real-Time Monitoring and Analysis
Data analytics allows security teams to monitor network traffic, system logs, and other data sources in real-time, enabling them to detect potential threats and respond quickly to mitigate the impact of an attack.
2. Identifying Potential Security Risks
Data analytics can help organizations identify potential vulnerabilities and risks by analyzing data from various sources, such as network logs, system logs, and security devices. This allows them to take proactive measures to mitigate these risks before they can be exploited by attackers.
3. Predictive Modeling
Data analytics can be used to develop predictive models that identify potential threats before they even occur. By analyzing historical data and identifying patterns and trends, security teams can predict potential threats and take proactive measures to prevent them.
4. Behavioral Analytics
Data analytics can be used to identify unusual user behavior, which may indicate a potential security threat. By monitoring user activities and analyzing data from various sources, security teams can identify anomalies and take appropriate action to mitigate the threat.
5. Threat Intelligence
Data analytics can be used to analyze external data sources, such as threat intelligence feeds, to identify potential security threats. By combining external data with internal security data, organizations can gain a more comprehensive view of their security posture and identify potential threats.
Data Analytics vs. Cybersecurity
“Cybersecurity” is an umbrella term that covers any data protection from threats, while “data analytics” is a specific strategy used to make informed data-driven decisions on threat detection and remediation. Data analytics uses large amounts of information collected from various locations to feed ML algorithms. ML algorithms use data to provide insight into the health and security of an organization’s environment.
Data analytics can be a component in cybersecurity protection, but it’s not everything in a cybersecurity strategy. It’s one component in the various tools used to actively monitor networks, perform security research and remediate threats as they are found in the environment.
Although data analytics is just a component of cybersecurity, it’s also important for organizations to find tools and strategies that can work with large data silos. To help with data collection, small organizations work with cloud-based analytics that have their own data collection standards. For large organizations, cybersecurity staff will help build a solution around the current environment and find strategies that conform with compliance regulations.
Best Practices for Cybersecurity Analytics
Cybersecurity analytics is a critical component of a robust security posture. Here are some best practices:
Data Management
- Data Quality: Ensure data accuracy, completeness, and consistency.
- Data Enrichment: Correlate data from various sources to gain deeper insights.
- Data Retention: Define clear data retention policies to balance compliance and analysis needs.
Analytics Methodology
- Threat Intelligence Integration: Incorporate external threat intelligence to enhance detection capabilities.
- Behavior Analytics: Analyze user and system behavior to identify anomalies.
- Machine Learning: Utilize ML algorithms for pattern recognition and prediction.
- Incident Response Integration: Closely integrate analytics with incident response processes.
Tool Selection and Implementation
- Tool Evaluation: Select tools based on functionality, scalability, and integration capabilities.
- Data Integration: Ensure seamless data flow between different tools and systems.
- Regular Updates: Keep analytics tools and platforms up-to-date with the latest patches.
Team and Process
- Skilled Personnel: Invest in training and development of cybersecurity analysts.
- Collaboration: Foster collaboration between security, IT, and business teams.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and refine analytics processes.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan based on analytics insights.
Risk Management
- Risk Assessment: Prioritize threats based on potential impact and likelihood.
- Threat Modeling: Identify potential attack vectors and vulnerabilities.
- Mitigation Strategies: Develop strategies to address identified risks.
Compliance and Governance
- Data Privacy: Adhere to data privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA).
- Audit and Compliance: Implement regular audits to ensure compliance with security standards.
Additional Considerations
- Automation: Automate routine tasks to improve efficiency and reduce human error.
- Visualization: Use data visualization tools to communicate insights effectively.
- Threat Hunting: Proactively search for threats beyond known indicators.
- Security Awareness: Educate employees about cybersecurity best practices.
By following these best practices, organizations can significantly enhance their ability to detect, respond to, and prevent cyberattacks.
Applications of Cybersecurity Analytics
Cybersecurity analytics is a powerful tool for organizations to enhance their security posture. Here are some key applications:
Threat Detection and Prevention
- Anomaly Detection: Identifying unusual patterns in network traffic, user behavior, or system logs to uncover potential threats.
- Real-time Threat Monitoring: Continuously scanning for emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
- Incident Response: Analyzing security incidents to determine root cause, containment, and recovery strategies.
- Threat Hunting: Actively searching for hidden threats within an environment.
Risk Assessment and Management
- Vulnerability Assessment: Identifying and prioritizing system weaknesses.
- Risk Prioritization: Assessing the potential impact of threats and allocating resources accordingly.
- Compliance Management: Ensuring adherence to industry regulations and standards.
Security Operations Center (SOC) Optimization
- Alert Triage: Prioritizing security alerts based on severity and potential impact.
- Incident Investigation: Accelerating incident response through automated data analysis.
- Mean Time to Detect (MTD) and Mean Time to Respond (MTTR) Reduction: Improving overall security efficiency.
Insider Threat Detection
- User Behavior Analytics (UBA): Monitoring user activities to identify suspicious behavior.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Preventing sensitive data exfiltration.
- Access Control Optimization: Enhancing access controls based on user behavior analysis.
Fraud Detection
- Financial Fraud: Identifying fraudulent transactions and activities.
- Identity Theft: Detecting unauthorized access to personal information.
- Account Takeover: Preventing unauthorized access to online accounts.
Network Security
- Intrusion Detection System (IDS) Enhancement: Improving IDS accuracy through advanced analytics.
- Network Traffic Analysis: Identifying malicious network activity and data exfiltration attempts.
- Network Performance Optimization: Analyzing network performance to identify bottlenecks and optimize resources.
Cloud Security
- Cloud Infrastructure Protection: Monitoring cloud environments for threats and vulnerabilities.
- Data Security: Protecting sensitive data stored in the cloud.
- Compliance Enforcement: Ensuring adherence to cloud security standards and regulations.
Industrial Control Systems (ICS) Security
- Anomaly Detection: Identifying abnormal behavior in ICS systems.
- Threat Hunting: Actively searching for threats in ICS environments.
- Incident Response: Responding to ICS-specific security incidents.
By effectively applying cybersecurity analytics, organizations can significantly strengthen their security posture, reduce risks, and protect their valuable assets.
Cybersecurity Analytics is the New Generation of Cybersecurity
These days, there are many robust cybersecurity analytics engines out there that deliver threat detection and security monitoring, in real-time.
These cybersecurity protocols, once naively considered a nice-to-have, are now critical to a business’ survival. It signifies your business’ growth from a protection mindset to one of detection.
The right cybersecurity analytics platform provides your business with a holistic view of your cybersecurity: a full history of your business’ cyber security processes and threats, coupled with broader industry issues.
But it also allows you to undertake threat hunting in real-time, providing an immediate alert so you’re prepared against any malware attacks and present threats.
Cybersecurity analytics is also a smart way to communicate to executive teams, management, and stakeholders. The data it gathers allows your security teams to access real time analytics and results, and provide insights that demonstrate the value your security solutions are delivering.

Machine Learning & Predictive Analytics in Cybersecurity
AI and machine learning technologies are rapidly advancing, and as it does, we’re taking advantage of these exciting advances and applying them to improving information security. Cyber security practices are quickly taking what was previously science fiction, and turning it into science fact.
Cybersecurity analytics platforms use powerful algorithms to gather and analyse data from a range of cyber security systems. They collect and study historical cyber security threat and attack data, and once it’s gathered, sorted, and analysed, it’s translated into predicting patterns of cyber threats.
And the more attacks there are, the more relevant data is gathered, the more informed analytics become—the more precise they can be in predicting future attacks before they occur.
This works in real-time, too. These data-driven models are used to collect and analyse information and analyse patterns, casting a historic lens over the data to determine where current patterns match historical threat patterns.
Cyber Data Analysts
Cyber data analysts will become invaluable in how you deploy a security solution. They’re the drivers behind your analytics deployment, and will work with you to:
- Define the needs of your cyber security data analytics platforms and processes, dig through the available information to identify threats and vulnerabilities your business faces;
- Analyse the available data to determine the manner of solution you require;
- Report on their findings, and deliver recommendations for deploying security data analytics; and
- Come on board to roll out the process for you as an embedded part of your security teams.

Conclusion
Cybersecurity analytics has emerged as an indispensable tool in the ongoing battle against cyber threats. By harnessing the power of data, organizations can gain invaluable insights into their security posture, proactively identify vulnerabilities, and respond effectively to incidents.
Through applications in threat detection, risk assessment, incident response, and beyond, cybersecurity analytics empowers organizations to:
- Enhance threat visibility: Identify and prioritize emerging threats.
- Optimize security operations: Improve efficiency and effectiveness of security teams.
- Reduce risk exposure: Proactively address vulnerabilities and mitigate potential damage.
- Accelerate incident response: Streamline investigation and recovery processes.
- Support compliance: Ensure adherence to industry regulations and standards.
However, it’s essential to recognize that cybersecurity analytics is not a standalone solution. It requires integration with other security measures, skilled personnel, and a continuous improvement mindset.
As the threat landscape continues to evolve, cybersecurity analytics will play an increasingly critical role in safeguarding digital assets. By embracing this technology and best practices, organizations can build a more resilient and secure future.
FAQs
Cybersecurity analytics involves aggregating data for the purpose of collecting evidence, building timelines, and analyzing everything in order to design a proactive strategy for cybersecurity.
With cybersecurity analytics, your network security is able to detect threats before they impact your system. It can also manage large amounts of data and process it to identify and mitigate threats.