Gartner defines cybersecurity mesh architecture (CSMA) as “a composable and scalable approach to extending security controls, even to widely distributed assets. Its flexibility is especially suitable for increasingly modular approaches consistent with hybrid multicloud architectures. CSMA enables a more composable, flexible, and resilient security ecosystem. Rather than every security tool running in a silo, a cybersecurity mesh enables tools to interoperate through several supportive layers, such as consolidated policy management, security intelligence and identity fabric.”

Cyber Security Mesh Architecture
CSMA has four foundational layers to configure and manage distinct security services.
- Security analytics and intelligence: Collecting and analysing security data from security tools with the help of a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tool will provide real-time threat notifications.
- Distributed identity fabric: Decentralized directory services, which are essential to a zero-trust paradigm, are prepared and provided to the security system. These include user entitlement management, adaptive access, identity proofing, and decentralized systems.
- Consolidated policy and posture management: Configuring individual security tools by translating a central policy into the native configuration constructs to ensure consistent and standardized security policies among the security systems.
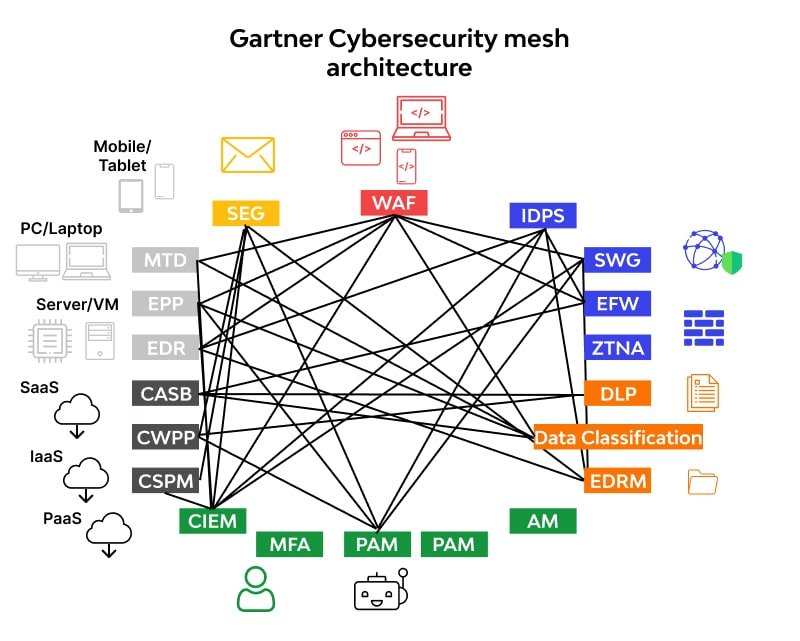
The Layers of Cybersecurity Mesh
Adopting a cybersecurity mesh strategy has distinct advantages, specifically scalability, composability, and interoperability. For new developments, this strategy changes the approach to designing and building the network infrastructure. For existing networks, evolving to a new strategy may mean significant adjustments to the infrastructure at first, but the benefits justify the cost.
1. Security Analytics and Intelligence
Centralized administration means that vast amounts of data can be collected, consolidated, and analyzed in real-time at a central location. This improves your risk analysis capabilities, threat response time, and mitigation of attacks. CSMA “combines the data and lessons from other security tools, and provides analyses of threats and triggers appropriate responses.”
2. Distributed Identity Fabric
This layer “provides capabilities such as directory services, adaptive access, decentralized identity management, identity proofing and entitlement management.”
3. Consolidated Policy and Posture Management
CSMA “can translate a central policy into the native configuration constructs of individual security tools or, as a more advanced alternative, provide dynamic runtime authorization services,” ensuring IT teams can more effectively identify compliance risks and misconfiguration issues.
Cybersecurity Mesh Principles
A Zero Trust Architecture approach verifies and authenticates, regardless of the network location or user/device identity.
A Decentralized approach ensures security controls are distributed across the network as opposed to being centralized at one location. This makes it possible for a more robust and flexible security posture.
An Interoperability aspect encourages communication and cooperation among various security platforms and solutions, enabling the sharing and integration of security data with ease.
Why Enterprises Need Cybersecurity Mesh
Cybersecurity mesh is the most practical and adaptable approach for dealing with these threats in an enterprise-level organization. It extends security across your entire architecture, making it possible to secure all systems and points of access with a single, unified set of technologies. Further, because it is driven by the most recent threat intelligence, a cybersecurity mesh can evolve as new threats emerge.
- Using third-party apps and services. Part of strengthening the core of an organization’s business is integrating third-party applications and services. In this way, the distributed nature of cybersecurity mesh allows companies to increase market share and engage consumers more rapidly while minimizing their security investments.
- Establishing new distribution channels. Third-party partnerships often lead to new channels for the distribution of products and services. Deploying individual security tools to protect the architecture needed to support new distribution channels can be costly and complicated. Using a cybersecurity mesh approach eliminates some of the cost and complexity.
- Launching new initiatives. Agile businesses may see opportunities to launch new initiatives that involve additions to their network infrastructure. This requires the kind of flexibility you get with a cybersecurity mesh.
Applications of Cybersecurity Mesh
- Increased Flexibility and Adaptability: Cybersecurity mesh enhances organizational flexibility and adaptability, bolstering overall security measures. By centralizing security policy management, organizations can implement a flexible system capable of accommodating diverse designs simultaneously, facilitating scalability and growth as needed.
- Enhanced Security Integration: Integrating security systems with the network via Cybersecurity Mesh Architecture (CSMA) offers additional security enhancements. By safeguarding all inbound and outbound network traffic, CSMA inherently fortifies network security, providing:
- Preparedness for Future Threats: Adoption of cybersecurity technologies conducive to seamless integration ensures readiness to address emerging security threats. Plug-in application programming interfaces (APIs) enable easy modifications and expansions, enhancing adaptability.
- Remediation of Security Gaps: Leveraging both legacy and modern security standards helps address security vulnerabilities stemming from disparate solutions.
- Optimization of CSMA Layers: Utilizing key components of CSMA such as security analytics, identity mesh, policy management, and built-in tools provides a comprehensive security framework, offering holistic protection from inception to implementation.
Key Considerations When Adopting Cybersecurity Mesh
- Vulnerability. There has been a 600% increase in phishing schemes over the past couple of years, and ransomware attacks occur every 11 seconds. This exposes the reality that current IT systems are vulnerable. In addition to existing vulnerabilities, there is the threat of a zero-day attack, an attack by a method previously unknown.
- Cost. The cost of ransomware attacks alone is about $6 trillion annually, and the cost of cybercrime attacks is on the rise at about 15% per year. Digital transformation incurs its own cost, too, especially if an organization’s infrastructure or architecture has to be redesigned. But the reduction in costly attacks and company downtime realized by leveraging cybersecurity mesh far outweighs any initial cost.
- Migration. Meeting the needs of clients and consumers has caused an accelerated shift to cloud computing platforms. However, it can also result in breaches. Cybersecurity mesh enables migration by providing flexible and scalable protection for cloud computing environments.
These factors highlight the need for cybersecurity mesh, but there are other factors that make the cybersecurity mesh option attractive:
- Ease of implementation. Digitalization has accelerated exponentially in recent years. This rate of growth can render traditional security models top-heavy and cumbersome. Cybersecurity mesh is uniquely suited to make design, deployment, and maintenance simple and efficient.
- Practicality. Cloud-based applications, distributed data, and uncontrolled devices all complicate traditional security policies and techniques. Therefore, a cybersecurity mesh strategy is a more practical model for dealing with components of an organization’s digital assets that lie outside the traditional network perimeter.
- Agility. The nature of the cybersecurity mesh approach is that it makes an organization’s response to security and expansion more agile. Nodes can be added or removed with relative ease, new locations can be monitored and controlled from a central control point, and threat response and mitigation can more easily mitigate an attack.
Advantages of Cybersecurity Mesh
A cybersecurity mesh is a distributed architectural approach that provides flexible, scalable, and reliable cybersecurity control.
Enhanced Flexibility and Adaptability
- Customization: The mesh allows for tailored security controls based on individual devices or users, ensuring optimal protection without over-burdening systems.
- Dynamic Response: It enables quick adaptation to changing threat landscapes and organizational needs.
Improved Security Posture
- Distributed Defense: By distributing security controls across the network, it creates a more resilient defense against attacks.
- Proactive Threat Detection: The mesh can detect and respond to threats in real-time, reducing the risk of breaches.
- Data Protection: It safeguards sensitive data by providing multiple layers of protection.
Operational Efficiency
- Simplified Management: Centralized management of security policies simplifies operations.
- Faster Incident Response: Rapid detection and response to threats minimize downtime.
- Cost-Effective: The mesh can optimize resource allocation by focusing protection on high-value assets.
Disadvantages of Cybersecurity Mesh
Complexity and Management
- Increased Complexity: Implementing and managing a cybersecurity mesh can be complex due to the multitude of interconnected components.
- Skill Requirements: Requires specialized skills and expertise to design, implement, and maintain the mesh effectively.
Cost and Resource Intensive
- Higher Initial Investment: Implementing a cybersecurity mesh can be costly due to the need for new infrastructure, software, and personnel.
- Ongoing Expenses: Maintaining and updating the mesh requires continuous investment in technology and human resources.
Interoperability Challenges
- Integration Difficulties: Integrating different security tools and technologies into a cohesive mesh can be challenging.
- Vendor Lock-In: Reliance on specific vendors might limit flexibility and increase costs.
Potential for Overlap and Redundancy
- Inefficient Resource Allocation: Without proper planning, there’s a risk of overlapping security controls, leading to inefficiencies.
- Increased Management Overhead: Managing redundant security measures can add complexity and overhead.
Data Privacy Concerns
- Data Sharing Risks: Sharing data across multiple security components might increase the risk of data breaches.
- Compliance Challenges: Adhering to data privacy regulations can be more complex in a mesh environment.
Digital transformation that highlight the need for cybersecurity mesh
The acceleration of digital transformation and innovation has caused a whirlwind of evolution in the cyber needs of organizations of various sizes. Keeping up with existing threats and preparing for zero-day threats has become more complex and challenging. As a result, an organization must unify its protection tools so they cover all access and endpoints. With cybersecurity mesh, security policies can be applied to all segments of your environment.
Firewalls and network control tools ensure that a particular area is independently safe and not a threat to the rest of the infrastructure. Cybersecurity controls can be delivered and managed through the cloud from a single control point. By centralizing controls in this way, an organization can reduce their IT staff expenditure, including the workstations they would need to manage disparate solutions. Additionally, you can use one control center—managed by a single individual or small team.
What are the challenges of cybersecurity mesh?
While cybersecurity mesh offers significant advantages in flexibility and adaptability, it also presents several challenges:
Technical Challenges
- Complexity: Integrating various security components into a cohesive mesh requires significant expertise and careful planning.
- Interoperability: Ensuring seamless communication and data sharing between different security tools and platforms can be complex.
- Data Management: Managing the vast amount of security data generated by the mesh can be overwhelming.
- Scalability: The mesh architecture must be able to adapt to changing organizational needs and growing attack surfaces.
Organizational Challenges
- Skill Gap: Organizations may lack the necessary skills to design, implement, and manage a cybersecurity mesh.
- Cultural Shift: Adopting a decentralized security approach requires a change in mindset for security teams.
- Vendor Management: Managing multiple security vendors and their solutions can be complex and time-consuming.
- Cost: Implementing a cybersecurity mesh can be expensive due to the need for new technologies and skilled personnel.
Security Challenges
- Visibility: Maintaining comprehensive visibility across the entire distributed environment can be challenging.
- Risk Management: Assessing and managing risks across a distributed network can be complex.
- Incident Response: Coordinating incident response across multiple security domains can be difficult.
Additional Challenges
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring compliance with various regulations in a distributed environment can be complex.
- User Experience: Balancing security with user experience can be challenging, especially in a remote work environment.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of a cybersecurity mesh often outweigh the drawbacks, making it a promising approach for organizations facing complex and evolving threat landscapes.
Implementing Cybersecurity Mesh
- Creating an integrated framework where security solutions can work together in synergy to achieve interoperability.
- Choosing security solutions that have an open policy framework to ensure compatibility with the overall framework than independent devices.
- Choosing zero trust network access integrated with an access management tool over traditional VPN services for reliability and security.
- Proper Audit process and procedure that follows the Zero Trust framework so that only authorized users have access to assets.
- Choosing vendors who are responsive and flexible to incorporate custom changes to secure the environment quickly.
How does it impact your business?
Cybersecurity Mesh (CSM) is a transformative approach to safeguarding your business in today’s digital landscape. By creating a network of interconnected security controls, CSM offers a robust defense against evolving cyber threats. This decentralized architecture allows for greater flexibility and adaptability, enabling businesses to respond swiftly to emerging challenges.
The impact of CSM extends beyond enhanced security. It empowers organizations to operate more efficiently by optimizing resource allocation and minimizing downtime. By proactively identifying and addressing vulnerabilities, CSM helps prevent costly data breaches, protecting your business reputation and customer trust. Additionally, as the business landscape continues to evolve, with remote work and cloud adoption becoming commonplace, CSM’s ability to adapt to changing environments is invaluable.
Ultimately, cybersecurity mesh is an investment in your business’s resilience. By implementing CSM, you’re not only safeguarding your digital assets but also creating a foundation for sustained growth and success.

Cybersecurity Mesh Jobs
Cybersecurity mesh jobs are on the rise as organizations adopt this distributed security architecture. Roles span from designing and implementing mesh networks to managing security operations within this complex environment. Professionals with expertise in networking, cloud computing, microservices, and security orchestration are in high demand. As cybersecurity mesh becomes more prevalent, we can expect a wider range of specialized positions to emerge, offering exciting career opportunities for those looking to shape the future of cybersecurity.
To break into cybersecurity mesh jobs, individuals should focus on developing a strong foundation in traditional cybersecurity, combined with emerging technologies like cloud computing and microservices. Certifications in network security, cloud security, and cybersecurity architecture can be valuable assets. Additionally, gaining practical experience through projects or internships can provide a competitive edge. As the cybersecurity mesh landscape continues to evolve, staying updated on industry trends and advancements is essential for career growth.

Threats and Vulnerabilities in Cybersecurity Mesh
Cybersecurity Mesh (CSM) introduces a distributed approach to security, offering enhanced flexibility and adaptability. However, this distributed architecture also presents unique challenges. While CSM provides multiple layers of protection, it can increase complexity, making it difficult to manage and configure effectively. This complexity can lead to misconfigurations, creating vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. Additionally, the reliance on multiple interconnected components can introduce single points of failure. If one component is compromised, it can impact the overall security posture of the network.
Data privacy is another critical concern in CSM environments. Sharing sensitive information between different security components increases the risk of data breaches. Ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations across multiple jurisdictions can be complex and time-consuming. Moreover, the distributed nature of CSM can make it challenging to maintain visibility across the entire environment. Identifying and responding to threats can be hindered by the lack of a centralized view of security data. This reduced visibility can slow down incident response times and increase the potential damage from attacks.
To mitigate these risks, organizations must invest in robust security management tools, employee training, and incident response plans. Implementing strong access controls, encryption, and data loss prevention measures is crucial. Regular security assessments and audits can help identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses. By adopting a proactive approach and staying updated on the latest threats, organizations can effectively manage the risks associated with cybersecurity mesh and protect their valuable assets.
Conclusion
Understanding cybersecurity mesh is crucial in today’s digital landscape to strengthen organizational defenses against evolving cyber threats. As businesses continue to adopt dispersed architectures and cloud-based technologies, the need for a flexible and adaptive security framework like cybersecurity mesh becomes important. By using cybersecurity mesh, organizations can achieve improved threat detection, faster incident response times, and more efficient policy management, ultimately strengthening their overall security posture.
Cybersecurity Mesh (CSM) offers a promising approach to securing complex and dynamic IT environments. By distributing security controls and creating micro-perimeters, it enhances adaptability and responsiveness to evolving threats. However, CSM is not without its challenges. It introduces increased complexity, data privacy concerns, and visibility challenges. To effectively leverage CSM, organizations must invest in robust security management, employee training, and incident response capabilities. While CSM is not a silver bullet, it can be a valuable component of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy when implemented and managed thoughtfully.
FAQs
Unlike traditional security models, cybersecurity mesh emphasizes decentralized security controls and interoperability among security tools, enabling more adaptive and resilient defense mechanisms.
Implementing cybersecurity mesh offers benefits such as improved threat detection accuracy, faster incident response times, enhanced policy management efficiency, and more flexible access controls.
Cybersecurity mesh adapts to the dynamic nature of distributed architectures and cloud environments by providing a unified security framework that can protect assets across diverse and interconnected infrastructures.
