Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is the practice of detecting and preventing data breaches, exfiltration, or unwanted destruction of sensitive data. Organizations use DLP to protect and secure their data and comply with regulations.
The DLP term refers to defending organizations against both data loss and data leakage prevention. Data loss refers to an event in which important data is lost to the enterprise, such as in a ransomware attack. Data loss prevention focuses on preventing illicit transfer of data outside organizational boundaries.

Why is DLP important?
DLP is essential in today’s digital landscape due to the increasing risks of data breaches, regulatory fines, and reputational damage. Data breaches can lead to several negative outcomes, including:
- Damage to reputation
- Higher customer turnover
- Loss of revenue from system downtime
- Extra costs of acquiring new customers to fill the gap created by a weakened reputation
In addition to the financial implications of data breaches, organizations must also consider the importance of maintaining customer trust and protecting intellectual property.
Do I Need Data Loss Prevention
Data loss prevention solves three main objectives that are common pain points for many organizations: personal information protection compliance, intellectual property (IP) protection, and data visibility.
Personal Information Protection Compliance: If so, you are more than likely subject to compliance regulations, such as HIPAA and GDPR (for personal data of EU residents), that require you to protect your customers’ sensitive data. DLP can identify, classify, and tag sensitive data and monitor activities and events surrounding that data. In addition, reporting capabilities provide the details needed for compliance audits.
IP Protection: DLP solutions like Digital Guardian that use context-based classification can classify intellectual property in both structured and unstructured forms. With policies and controls in place, you can protect against unwanted exfiltration of this data
Data Visibility: A comprehensive enterprise DLP solution can help you see and track your data on endpoints, networks, and the cloud. This will provide you with visibility into how individual users within your organization interact with data.
How does data loss prevention work?
DLP software monitors, detects and blocks sensitive data from leaving an organization. That means monitoring both data entering an organization’s networks as well as data leaving the network.
Most DLP software focuses on blocking actions. For example, if an employee tries to forward a business email outside the corporate domain against company policy, or they try to upload a corporate file to a consumer cloud storage service such as Dropbox also against company policy, permission would be denied.
Detection primarily centers on monitoring incoming emails to look for suspicious attachments and hyperlinks that indicate phishing attacks. Most DLP software will flag inconsistent content for staff to manually examine or the system can block questionable content outright.
In the early days of DLP, security teams set the rules around detection and blocking, but those were simplistic and often circumvented. Newer software uses machine learning-based artificial intelligence, which can learn and improve detection and blocking over time. These tools can automate responses and provide near real-time monitoring and alerts.
Types of DLP solutions
Three primary types of DLP solutions are available: network, endpoint, and cloud. Each of these solutions provides distinct data protection capabilities, catering to the unique needs and requirements of organizations.
Network
Network DLP solutions focus on protecting data in transit within an organization’s network, monitoring and controlling data flows.
By safeguarding data as it traverses networks, including the internet, intranets, and extranets, network DLP solutions help organizations maintain control over their sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access. Network DLP software provides additional benefits, such as:
- Increased visibility into network traffic
- Content inspection to prevent unauthorized access or exfiltration of sensitive information
Endpoint
Endpoint DLP solutions protect data at the user level by monitoring and controlling data access and usage on devices such as laptops, desktops, and mobile devices.
These solutions focus on preventing data leakage from endpoint devices, allowing organizations to maintain control over their sensitive information and ensure that it is not misused or mishandled. Endpoint DLP solutions detect potential data leaks by monitoring data transfers, such as emails, file uploads/downloads, USB storage device usage, and printer access.

Cloud
Cloud DLP solutions are designed to safeguard data stored and processed in cloud-based systems, helping organizations comply with data protection regulations and blocking unauthorized access.
For example, Cloud DLP solutions protect common cloud-based applications such as Office 365, G Suite, Box, and Dropbox.
As more organizations move their data and applications to the cloud, robust cloud DLP solutions have become increasingly crucial. Cloud DLP provides the following capabilities for data in the cloud:
- Scanning
- Discovering
- Classifying
- Reporting
Cloud DLP solutions enable organizations to protect sensitive data stored in the cloud while ensuring compliance with data protection regulations. This provides double benefits: maintaining control over their data while leveraging the benefits of cloud-based environments.
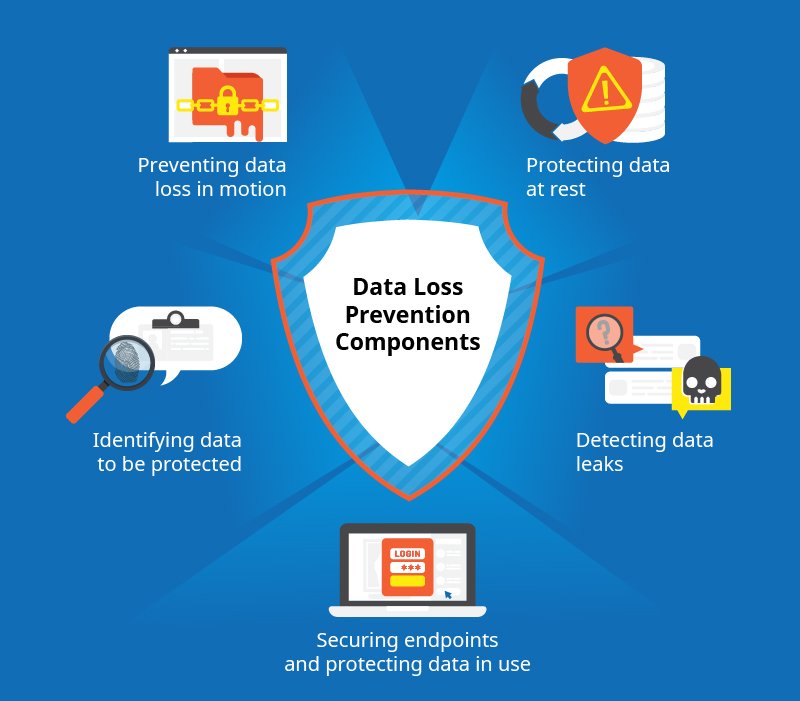
Data Loss Prevention Components
Data loss prevention can be broken down into the following components:
Preventing data loss in motion Data in motion or network traffic is protected by the network technology, which is typically installed at network egress points near the perimeter. The central management server analyzes network traffic from multiple security control points and looks for sensitive data that is sent in violation of information security policies.
Securing endpoints and protecting data in use Data while in use or endpoint systems run on internal end-user workstations or servers. End-point based technology (just like a network technology) addresses both internal as well as external communications and is used to control information flow between different groups and types of users.
Protecting data at rest Data at rest or data storage can be protected by access control and encryption with the appropriate data retention policies in place.
Identifying data to be protected Data identification technology, sometimes confused with data discovery, determines what data to look for and includes techniques aimed at identifying confidential and sensitive information.
Benefits of DLP
DLP platforms have advantages for organizations that manage sensitive data:
- Improving visibility and incident response. DLP platforms provide a user interface that lets users view the status of their data sources. These platforms typically send out alerts and expedite incident responses when there’s a data breach or cyberattack.
- Assisting with compliance. DLP platforms help organizations store, classify and use data in ways that comply with local, state and federal standards for handling sensitive data, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
- Limiting access to authorized personnel. DLP tools have authentication and access control features that only allow trusted employees to use sensitive data.
- Preventing data leaks. DLP reduces the likelihood that an organization will suffer a data breach or other attack, and thus be liable for financial costs or reputational harm associated with compromised or lost data.
Key components of a DLP strategy
Implementing a DLP strategy involves several key components. These components work together to create a strong foundation for data security, ensuring that sensitive data is:
- Identified
- Classified
- Monitored
- Protected from unauthorized access or misuse
Here’s what you need to know about each component
Data identification
Data identification is the initial step in a DLP strategy, as it involves locating and understanding the types of sensitive data an organization holds and where it resides. This process is essential for organizations to recognize what data they possess and how it should be managed.
Data classification
Data classification is another critical component of a DLP strategy. It involves categorizing data based on sensitivity and risk levels, so you can apply appropriate protection measures.
Monitoring and enforcement
Monitoring and enforcement play a critical role in the context of DLP, as they involve utilizing DLP tools to identify and avert potential data breaches, leaks, or misuse and executing data protection policies. DLP tools are employed to:
- Detect and forestall potential data breaches, leaks, or misuse
- Provide real-time monitoring and analytics capabilities
- Enable security teams to quickly identify and respond to potential threats
Continuous employee training & guidance
Offering ongoing employee training and guidance is essential to guarantee that employees are cognizant of the data protection policies and comprehend how to manage sensitive data appropriately.
Components of a Data Loss Solution
- Securing data in motion — technology installed at the network edge can analyze traffic to detect sensitive data sent in violation of security policies.
- Securing endpoints — endpoint-based agents can control information transfer between users, groups of users, and external parties. Some endpoint-based systems can block attempted communications in real time and provide user feedback.
- Securing data at rest — access control, encryption and data retention policies can protect archived organizational data.
Challenges of DLP
Despite its importance, implementing and effectively managing a DLP solution can present several challenges. Here are some of the most common:
1. False Positives and Negatives
- False positives: DLP systems may mistakenly flag legitimate activities as suspicious, leading to unnecessary disruptions and frustration among users.
- False negatives: Conversely, the system might fail to detect actual data breaches, compromising sensitive information.
2. Complexity and Overwhelm
- Multiple layers: DLP often involves integrating various components like endpoint protection, network security, and cloud security, making it complex to manage.
- Configuration challenges: Configuring DLP rules to effectively protect sensitive data while minimizing disruptions can be a daunting task.
3. Data Classification and Labeling
- Inconsistent labeling: Ensuring that data is accurately classified and labeled consistently across the organization can be difficult, especially for large datasets.
- Dynamic nature of data: Data can change rapidly, making it challenging to keep classifications up-to-date.
4. Employee Resistance and Adoption
- Privacy concerns: Employees may perceive DLP as an invasion of privacy, leading to resistance and reduced productivity.
- Training and education: Effective DLP implementation requires educating employees about data security best practices and the importance of compliance.
5. Evolving Threat Landscape
- New attack methods: DLP systems must constantly adapt to new and emerging threats, such as advanced persistent threats (APTs) and insider threats.
- Data exfiltration techniques: Hackers are continually developing new ways to steal data, making it difficult for DLP solutions to keep pace.
6. Cost and ROI
- Initial investment: Implementing a robust DLP solution can be expensive, requiring significant upfront costs.
- Ongoing maintenance: Maintaining and updating a DLP system over time also incurs costs.
- Measuring ROI: Quantifying the return on investment (ROI) of DLP can be challenging, as it involves intangible benefits like preventing data breaches and protecting reputation.
To overcome these challenges, organizations must adopt a comprehensive approach to DLP, including:
- Regular evaluation and tuning of DLP rules and policies.
- Ongoing employee education and awareness programs.
- Investment in advanced DLP technologies that can better detect and prevent threats.
- Collaboration with data security experts to ensure effective implementation and management.
DLP tools and software
DLP tools and software play a vital role in upholding data security policies and preventing data loss. Popular DLP tools include Digital Guardian DLP, Forcepoint DLP and Symantec Data Loss Prevention. These tools help organizations discover, classify, monitor, and protect sensitive data, ensuring that their data protection efforts are comprehensive and effective.
DLP tools and software offer a range of features and capabilities, such as:
- Integration with existing technology stacks
- Real-time monitoring
- Analytics
- Automated workflows

Experts Weigh in on Data Loss Prevention
Here’s a look at what the experts have to say about data loss prevention.
1. Data protection is everyone’s job. “Everyone in a company is responsible for upholding data security standards. While the IT department does the majority of the everyday work with these systems and processes, stakeholders across your organization influence security policy and implementation.
2. Encryption is important. “Security is more than encryption, of course. But encryption is a critical component of security. While it’s mostly invisible, you use strong encryption every day, and our Internet-laced world would be a far riskier place if you did not.
3. Be mindful of insider threats. “I’ve worked with organizations to prevent insider threats as well as in response to incidences. In my experience, the notion of it being ’easy’ to deter and detect insider threats is only the case if organizations are proactive about their approach in the first place.
Trends driving DLP adoption
More than 35% of all DLP implementations fail, according to Gartner. Such failure can lead to severe consequences for a business, including fines, penalties and a degraded reputation. It’s these factors that drive DLP adoption, including the following:
- Cost of a data breach. As previously mentioned, the average total cost of a data breach is nearly $4.5 million. The long-term costs related to reputational damage can be higher.
- Compliance. The growing list of global regulations — including PCI DSS, HIPAA and the EU-based General Data Protection Regulation — increases the need for DLP to help meet data governance legal requirements.
- Expanding data volumes. Companies produce more data than ever that generates a great deal of value. Sophisticated hackers are on the prowl to find ways to steal data for profit, including tactics such as identity theft, insurance fraud and other economic crimes.
- Chief information security officers (CISOs). Companies are hiring professional security specialists known as CISOs to create and oversee governance policies that secure intellectual property and other confidential data and information. CISOs typically use DLP as one of their security tools.
- Talent shortages. Skilled data security professionals are in demand and difficult to find. To compensate, organizations often outsource DLP to vendors that provide managed IT services.
- Wider attack surfaces. Cloud services, endpoint devices and third-party vendor tools are vulnerable to ransomware, malware and other cybersecurity threats.
- Insider threats. These can be intentional or malicious, but often they aren’t. Employees transmitting important data using various communications tools can unintentionally put data at risk.
Data Loss Prevention Examples
REA Group is a multinational digital advertising agency that addressed DLP while restructuring its IT policy amid global expansion. Since REA is a cloud-first company with 90% of systems being SaaS-based, it needed to achieve the desired ability to monitor cloud usage. For that specific purpose, REA partnered with McAfee and opted for McAfee’s MVISION Cloud solution, which helped them achieve the appropriate security levels and prevent data loss while expanding and scaling upward.
Accenture, a global leader in technology solutions and services, built their own DLP ecosystem. The company deployed DLP agents on every workstation to monitor the data flow and report back to the security center. Accenture also developed its own set of rules to red-flag, prevent, or block file transfer of client data when sent to unauthorized devices, as well as implemented email DLP to prevent potential leakage of sensitive data through emails.

Common challenges in DLP implementation
Despite the benefits of DLP, organizations often face common challenges in its implementation.
Disparate data
One challenge is the complexity of managing multiple data types and locations, as organizations must identify and protect data across a wide range of systems and platforms.
Human error
Additionally, the need for ongoing employee training and awareness can be a significant hurdle, as human error remains a leading cause of data breaches.
False positives
Another challenge in DLP implementation is the potential for false positives and negatives in detecting data breaches. False positives can lead to unnecessary alerts and wasted resources, while false negatives can allow data breaches to go undetected.
To overcome these challenges, organizations should invest in robust DLP solutions and continuously refine their policies and processes to ensure that their data protection efforts are both effective and efficient.
Best Practices for Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Effective DLP implementation requires a combination of technology, processes, and human factors. Here are some best practices to consider:
1. Comprehensive Assessment and Risk Analysis
- Identify sensitive data: Determine what data is most valuable to your organization and needs protection.
- Assess vulnerabilities: Evaluate potential risks and attack vectors that could lead to data loss.
- Prioritize protection: Focus on the most critical data and vulnerabilities first.
2. Clear Data Classification and Labeling
- Consistent labeling: Ensure that data is accurately classified and labeled consistently across the organization.
- Regular review: Periodically review and update data classifications to reflect changes in business needs and regulations.
- Automated labeling: Consider using automated tools to streamline the labeling process.
3. Robust DLP Policy and Procedures
- Clear policies: Develop comprehensive DLP policies that outline acceptable data usage, access controls, and incident response procedures.
- Employee training: Educate employees about the DLP policy and its importance in protecting sensitive information.
- Regular reviews: Periodically review and update policies to address changes in technology, regulations, and business practices.
4. Effective DLP Technology
- Choose the right tools: Select DLP solutions that align with your organization’s specific needs and budget.
- Centralized management: Implement a centralized DLP platform to simplify management and reporting.
- Regular updates: Keep DLP software up-to-date with the latest security patches and features.
5. User Education and Awareness
- Training programs: Provide comprehensive training to employees on data security best practices and the importance of compliance.
- Awareness campaigns: Conduct regular awareness campaigns to reinforce DLP policies and educate employees about potential risks.
- Feedback mechanisms: Encourage employees to report suspicious activity or concerns related to data security.
6. Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
- Regular reviews: Conduct periodic reviews of DLP performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Incident response: Develop a robust incident response plan to address data breaches promptly and effectively.
- Threat intelligence: Stay informed about emerging threats and adjust DLP measures accordingly.
7. Compliance with Regulations
- Understand requirements: Ensure that your DLP measures comply with relevant regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
- Regular audits: Conduct regular audits to verify compliance and identify areas for improvement.
- Documentation: Maintain documentation of compliance efforts to support audits and investigations.
Conclusion
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is a critical component of modern cybersecurity strategies. By implementing effective DLP measures, organizations can protect their sensitive information from unauthorized access, theft, and misuse.
Key benefits of DLP include:
- Reduced risk of data breaches: DLP helps prevent unauthorized data exfiltration, reducing the likelihood of costly breaches.
- Improved compliance: DLP can help organizations meet regulatory requirements and avoid fines.
- Enhanced data security: DLP provides a strong foundation for protecting sensitive data and maintaining organizational integrity.
- Strengthened trust: By demonstrating a commitment to data security, organizations can build trust with customers, partners, and employees.
To maximize the effectiveness of DLP, organizations should:
- Conduct a comprehensive risk assessment and identify sensitive data.
- Develop clear data classification and labeling policies.
- Implement robust DLP technologies.
- Educate employees about data security best practices.
- Continuously monitor and improve DLP measures.
- Stay informed about emerging threats and adjust DLP strategies accordingly.
FAQs
A DLP solution can help your organization ensure that sensitive information does not get accidentally or intentionally outside the corporate network or to a user without access. Sensitive data can be customers’ Personally Identifiable Information (PII), Protected Health Information (PHI) or Payment Card Information (PCI), the company’s Intellectual Property (IP) such as trade secrets, source code, etc.
DLP, or Data Loss Prevention, is a cybersecurity solution that detects and prevents data breaches. Since it blocks extraction of sensitive data, organizations use it for internal security and regulatory compliance.
