mail (short for electronic mail) is a digital method by using it we exchange messages between people over the internet or other computer networks. With the help of this, we can send and receive text-based messages, often an attachment such as documents, images, or videos, from one person or organization to another. In this article, we will understand the concept of email security, how we can protect our email, email security policies, and email security best practices, and one of the features of email is an email that we can use to protect the email from unauthorized access.
What is Email Security?
Email security is the practice of safeguarding email accounts and communications from unauthorized access, loss, or compromise. It involves a combination of technologies and practices to protect against various threats.
Email security refers to the steps where we protect the email messages and the information that they contain from unauthorized access, and damage. It involves ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of email messages, as well as safeguarding against phishing attacks, spam, viruses, and another form of malware. It can be achieved through a combination of technical and non-technical measures.
Why is email security important?
Protection of Sensitive Information
- Data breaches: Email is often used to share sensitive data like financial information, personal details, and confidential business documents. Strong email security prevents unauthorized access to this data.
- Identity theft: Phishing attacks can steal personal information, leading to identity theft and financial loss.
Financial Loss Prevention
- Fraudulent transactions: Cybercriminals can use email to trick individuals or businesses into transferring money to fraudulent accounts.
- Business disruption: Malware attacks can disrupt operations, leading to financial losses due to downtime and recovery efforts.

Reputation Protection
- Brand damage: A data breach or phishing attack can damage a company’s reputation, leading to loss of customer trust.
- Legal liabilities: Companies can face legal consequences for data breaches, including fines and lawsuits.
Productivity and Efficiency
- Time wastage: Spam and phishing emails can consume valuable employee time.
- System disruptions: Malware can slow down computer systems and networks, reducing productivity.
Types of Email threats
- Social Engineering: Think of it as digital manipulation. The bad guys sweet-talk or scare people into revealing confidential stuff. It’s like a cyber con artist pulling off a heist.
- Spear Phishing: This one’s like a sniper attack. Instead of casting a wide net, the attacker aims at specific individuals or organizations. They craft personalized emails, luring victims into their trap.
- Ransomware: Picture your files locked up in a digital vault. The villain—malicious software—holds them hostage until you pay a ransom. It’s like a cyber kidnapper!
- Malware: Sneaky software that infiltrates your computer without asking permission. It’s like a digital ninja wreaking havoc behind the scenes.
- Spoofing: Imagine someone wearing a disguise at a masquerade ball. Attackers forge email headers, making messages look legit—even when they’re not. Trust no masked stranger!
- Man-in-the-Middle Attack: Visualize a sneaky eavesdropper intercepting your messages. They can read, alter, or inject new content. It’s like a cyber spy messing with your convo.
- Data Exfiltration: Sophisticated thieves sneak into an organization’s email system. They swipe sensitive data—like secret recipes from a chef’s kitchen. Recipe theft, anyone?
- Denial of Service: Attackers flood email servers with a deluge of messages. Servers buckle under the pressure, like a dam bursting. Chaos ensues!
- Account Takeover: Imagine a cyber burglar breaking into your email house. They use your account to send spam, phishing emails, or snoop around your secrets.
- Identity Theft: Someone swipes your personal info—name, address, social security number. They wear your identity like a stolen cloak, committing digital crimes.
Advantage of Email Security
Protection of Sensitive Information
- Data Confidentiality: Ensures that sensitive information remains private and protected from unauthorized access.
- Data Integrity: Maintains the accuracy and completeness of data transmitted via email.
- Data Availability: Protects email data from loss or damage due to cyberattacks.
Financial Security
- Fraud Prevention: Safeguards against financial losses caused by phishing, BEC, and other email-based scams.
- Cost Reduction: Reduces expenses related to data breaches, legal fees, and reputational damage.
Operational Efficiency
- Increased Productivity: Minimizes time wasted on dealing with spam, phishing, and malware.
- Business Continuity: Ensures uninterrupted business operations by preventing email disruptions.
Reputation Protection
- Trust Building: Demonstrates a commitment to protecting customer and employee data.
- Brand Protection: Safeguards the company’s reputation from negative publicity associated with data breaches.
Compliance Adherence
- Regulatory Compliance: Helps organizations meet industry-specific regulations and standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
Disadvantage of Email Security
Cost
- Implementation Costs: Implementing robust email security measures can be expensive, especially for small businesses.
- Ongoing Maintenance: Maintaining security systems requires ongoing investments in software updates, hardware upgrades, and employee training.
Complexity
- Technical Expertise: Managing complex email security solutions often requires specialized IT knowledge.
- False Positives: Overly aggressive security measures can sometimes block legitimate emails, leading to productivity losses.
User Behavior
- Employee Error: Despite training, employees may still click on malicious links or attachments, compromising security.
- Password Management: Weak or reused passwords can weaken overall email security.
Evolving Threats
- Constant Adaptation: Cybercriminals are constantly evolving their tactics, making it challenging to stay ahead of threats.
Steps should be taken to Secure Email
- Choose a secure password: Password must be at least 12 characters long, and contains uppercase and lowercase letters, digits, and special characters.
- Two-factor authentication: Activate the two-factor authentication, which adds an additional layer of security to your email account by requiring a code in addition to your password.
- Use encryption: It encrypts your email messages so that only the intended receiver can decipher them. Email encryption can be done by using the programs like PGP or S/MIME.
- Keep your software up to date. Ensure that the most recent security updates are installed on your operating system and email client.
- Beware of phishing scams: Hackers try to steal your personal information by pretending as someone else in phishing scams. Be careful of emails that request private information or have suspicious links because these are the resources of the phishing attack.
- Choose a trustworthy email service provider: Search for a service provider that protects your data using encryption and other security measures.
- Use a VPN: Using a VPN can help protect our email by encrypting our internet connection and disguising our IP address, making it more difficult for hackers to intercept our emails.
- Upgrade Your Application Regularly: People now frequently access their email accounts through apps, although these tools are not perfect and can be taken advantage of by hackers. A cybercriminal might use a vulnerability, for example, to hack accounts and steal data or send spam mail. Because of this, it’s important to update your programs frequently.
Email Security Policies
An email security policy is a set of guidelines designed to protect an organization’s email communications. It addresses potential threats such as phishing, malware, and data breaches by establishing rules and behaviors for handling email.
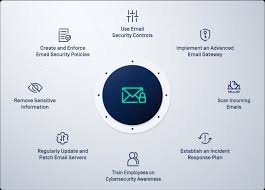
Components of an Email Security Policy
- Acceptable Use: Defines what constitutes appropriate email use within the organization, including restrictions on sending personal emails, using email for personal business, and sharing confidential information.
- Password Management: Outlines password requirements, such as complexity, length, and frequency of changes. It should also prohibit password sharing.
- Data Protection: Specifies how sensitive information should be handled, including encryption requirements, data classification, and authorized recipients.
- Malware Prevention: Describes measures to prevent malware infections, such as avoiding suspicious attachments and links, regularly updating antivirus software, and employee training.
- Phishing Awareness: Provides guidelines for recognizing phishing attempts, including suspicious email indicators and reporting procedures.
- Incident Response: Outlines steps to be taken in case of a security breach, including reporting procedures, containment measures, and recovery plans.
- Email Retention: Establishes guidelines for email retention and deletion, including legal and regulatory requirements.
Implementing an Effective Email Security Policy
- Clear and Concise: The policy should be easy to understand and follow.
- Enforced Consistently: The policy must be consistently applied to all employees.
- Regularly Reviewed and Updated: The policy should be updated to address emerging threats and changes in the organization.
- Employee Training: Employees should be educated about the policy and its importance.
what is email encryption
Email encryption is a security measure that transforms plain text email messages into a coded format, making them unreadable to anyone except the intended recipient.

How Does it Work?
Encryption involves using complex algorithms to scramble the content of an email. This process requires a cryptographic key, which is a unique piece of information that unlocks the encrypted message.
There are two main types of encryption:
- Symmetric Encryption: Uses the same key for both encryption and decryption.
- Asymmetric Encryption: Uses a pair of keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption.
Why is it Important?
Email encryption is crucial for protecting sensitive information like financial data, personal details, and confidential business communications. It helps prevent:
- Data breaches: Protects sensitive information from falling into the wrong hands.
- Identity theft: Safeguards personal information from being stolen.
- Unauthorized access: Prevents hackers from intercepting and reading your emails.
Email Security Capabilities and Tools
Email security is critical due to the prevalence of email-borne threats like phishing, malware, and spam. Effective email security involves a combination of technologies and processes to protect against these attacks.
Capabilities
- Threat Detection: Identifying malicious emails, attachments, and links.
- Malware Prevention: Blocking and removing malware from incoming and outgoing emails.
- Spam Filtering: Preventing unwanted emails from reaching inboxes.
- Phishing Protection: Identifying and blocking phishing attempts.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Protecting sensitive information from unauthorized disclosure.
- Encryption: Safeguarding email content with encryption.
- Email Continuity: Ensuring uninterrupted email services during outages.
Tools
Secure Email Gateways (SEGs): Filter incoming and outgoing email traffic for threats.
Anti-spam Filters: Block unwanted emails based on various criteria
.Anti-malware Software: Scan emails for malicious code
.Phishing Detection Tools: Identify phishing attempts using advanced techniques.
Email Encryption Solutions: Protect email content with encryption.
Email Archiving Systems: Store copies of emails for compliance and legal purpose.
User Education and Training: Empower employees to recognize and avoid email threats.
Dangers of Malicious Emails
Malicious emails can cause significant damage, not just to one’s device but to an entire network and the data connected to it. Just one ill-intended email can pose serious danger in a myriad of ways.
- Gain access to private information: Email is the most common way hackers trick users into accessing valuable information. It only takes one wrong click to enable a hacker to infiltrate your entire device and its contents.
- Infect your device with malware: Malicious code distributed in email messages can infect one or more devices by spreading ransomware attacks, crashing the victim’s system, providing threat actors with remote access to the device, stealing the victim’s personal data, destroying files, or adding the victim’s system to a malvertisement.
- Steal your data: A deceptively-fabricated email disguised as a legitimate or credible source can direct users to a phishing website – sometimes called a “spoof” or “lookalike” website – designed to steal your data. When victims enter their information, the site captures it and sends it to the attacker.
- Cause your computer to download more malware: Malware-infected email attachments often include code or exploits that make devices download more malware. These attachments are generally small, customized, and not widely spread, making them difficult to identify by standard anti-virus solutions.
- Put organizations at risk: Malicious emails can inflict immense damage on organizations by infecting other devices on the network, stealing sensitive data, or disrupting operations.
- It’s critical to be cautious when receiving emails from unknown senders or emails that seem suspicious. Avoid clicking links or downloading attachments from these emails, and delete them immediately. Educating yourself and your employees on how to identify malicious email messages is one of the most important things you can do to enforce effective email and data security protocols.
How Secure Is Email?
Email may seem like a fairly secure method of communication, given that access to it is password-protected. In reality, though, emails are exposed at various stages, and not just as far as you and your password are concerned. This may allow fraudsters to commit identity theft and fraud.
How secure is your email?
There are four key areas that fraudsters could target in order to gain access to your email:
- User’s devices, such as your laptop, tablet or smartphone
If you leave your devices unlocked and unattended, someone else could easily try to access your email. They’ll succeed if you’re already logged on to your email account, or if your password’s saved on your device, or easy to guess. Fraudsters who don’t have physical access to your devices can still have other tricks up their sleeves for accessing your email, such as by phishing. - Networks
Identity thieves don’t need access to your email account itself in order to gain access to your correspondence. They could target the connection between your device and your email provider, between your email provider and the recipient of your email, or between the recipient’s device and their email provider. - The servers that hold the emails
Servers physically store data that make up your emails. Identity thieves with access to email servers could gain access to not just the emails currently sitting in your inbox; they could potentially also get hold of your email attachments, or even some emails that you’d recently deleted.
How Proofpoint Can Help
Email security is a critical aspect of any organization’s cybersecurity strategy. Proofpoint provides comprehensive email security tools to anticipate and protect against today’s most advanced and pervasive email threats.
- Proofpoint Email Protection: Proofpoint Email Protection is the industry-leading email gateway, which can be deployed as a cloud service or on-premises. It catches both known and unknown threats that other email security systems miss. Powered by NexusAI – Proofpoint’s advanced machine learning technology – Email Protection accurately classifies various types of threats and provides multilayered detection techniques, including reputation and content analysis, to block malicious email.
- Proofpoint Email Isolation: Proofpoint Email Isolation enables IT and security teams to allow users to access personal webmail from corporate devices without security concerns.
- Proofpoint Email Encryption: Proofpoint Email Encryption uses policy-based encryption to make secure communication via messages and attachments seamless and automated for end-users.
- PhishAlarm: Administrators can access Proofpoint’s PhishAlarm email reporting button and PhishAlarm Analyzer email analysis tools. These tools provide complete visibility across email, instant messages, collaboration tools, voice, SMS, and social media.
Proofpoint is designed to help businesses identify and block threats using advanced machine learning technology and multilayered detection techniques. These are just some of the email security tools and features that Proofpoint delivers. Learn more about what makes Proofpoint a #1 ranked Email Security and Protection solution.
Conclusion
Email security is an indispensable component of modern communication and data protection. It safeguards sensitive information, prevents financial losses, and preserves organizational reputation.
By understanding the various threats, implementing robust security measures, and educating users, individuals and businesses can significantly reduce the risk of email-related cyberattacks.
Threat awareness: Recognizing the different types of email threats helps in developing effective countermeasures
.Security policies: Clear and enforced policies provide a framework for email security practices.
Encryption: Protecting email content through encryption is essential for data confidentiality.
User education: Training employees to identify and avoid phishing attacks is vital.
FAQs
The reason for which Email Security is important is protecting the organization’s business data. We should take necessary steps priorly to safe our business data.
For Cybercriminals, email attacks are so common for making cyber threats, thus email security is much important in modern days.