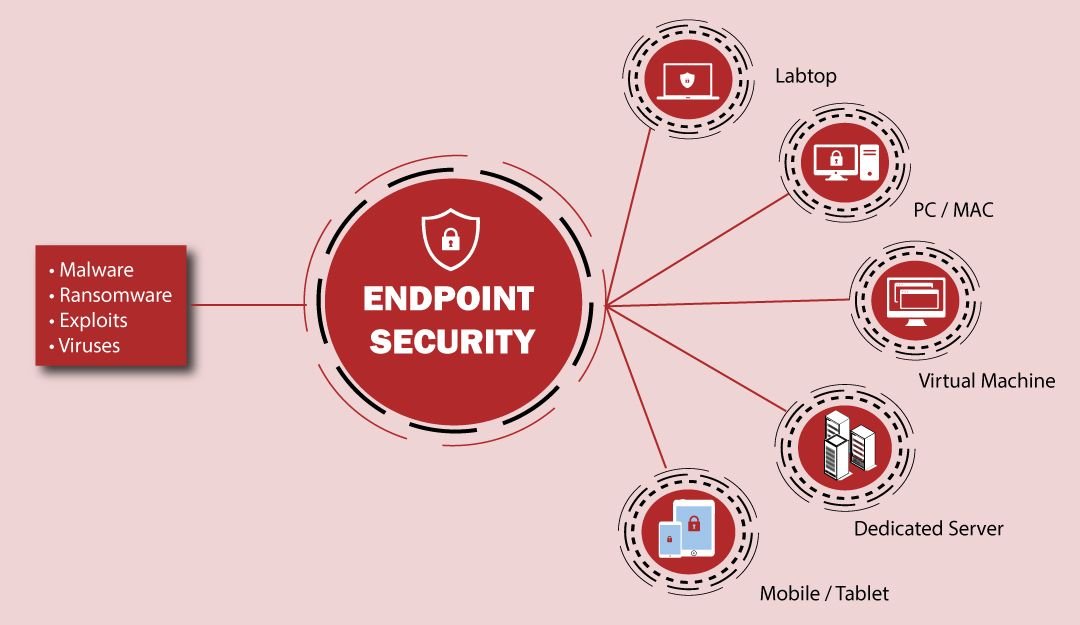
Endpoint security is the process of protecting devices like workstations, servers, and other devices (that can accept a security client) from malicious threats and cyberattacks. Endpoint security software enables businesses to protect devices that employees use for work purposes or servers that are either on a network or in the cloud from cyber threats.
Why endpoint security is important
An endpoint protection platform is a vital part of enterprise cybersecurity for several reasons. First of all, in today’s business world, data is the most valuable asset of a company —and to lose that data, or access to that data, could put the entire business at risk of insolvency. Businesses have also had to contend with not only a growing number of endpoints, but also a rise in the number of types of endpoints.
Benefits of Endpoint Security
ndpoint security is crucial for protecting your organization’s valuable data and systems from cyber threats. Here are some of the key benefits:
Protection Against Cyber Threats
- Malware Prevention: Protects against viruses, ransomware, spyware, and other malicious software.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Prevents unauthorized access, modification, or deletion of sensitive data.
- Phishing Protection: Safeguards against email-based attacks and fraudulent activities.
Improved Security Posture
- Enhanced Visibility: Provides insights into endpoint activity, helping identify potential threats.
- Risk Reduction: Minimizes the likelihood of successful cyberattacks.
- Compliance Adherence: Helps meet industry regulations and standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
Business Continuity
- Reduced Downtime: Minimizes system disruptions caused by security incidents.
- Financial Protection: Safeguards against financial losses due to data breaches and ransomware attacks.
- Reputation Protection: Protects your organization’s brand and customer trust.
Other Benefits
- Centralized Management: Streamlines security management across multiple endpoints.
- Remote Work Support: Protects devices used by remote employees.
- Incident Response: Provides tools for rapid response to security incidents.
Endpoint Security Solutions
Endpoint security solutions are a combination of hardware, software, and processes designed to safeguard your endpoints (computers, laptops, tablets, and mobile devices) from cyber threats.
Core Components of Endpoint Security Solutions
- Antivirus and Antimalware Protection: Detects and removes malicious software.
- Data Encryption: Protects data at rest and in transit.
- Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS): Identifies and blocks threats.
- Firewall Protection: Controls network traffic in and out of the device.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Continuously monitors endpoints for suspicious activity, detects threats, and enables rapid response.
Types of Endpoint Security Solutions
- Endpoint Protection Platform (EPP):
- Offers traditional antivirus protection, firewall, and intrusion prevention.
- Protects against known threats but may struggle with advanced attacks.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR):
- Focuses on detecting and responding to advanced threats.
- Provides in-depth visibility into endpoint activity and incident response capabilities.
- Extended Detection and Response (XDR):
- Combines EDR with other security solutions (e.g., network security, cloud security) for a unified view of threats across the entire environment.
Additional Considerations
- Mobile Device Management (MDM): Essential for managing and securing mobile devices.
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): Detects anomalies in user behavior to identify potential threats.
- Patch Management: Ensures software is up-to-date to address vulnerabilities.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Protects sensitive data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, duplication, modification, or destruction.
Choosing the Right Solution
The best endpoint security solution depends on your organization’s size, industry, risk tolerance, and budget. Consider the following factors:
- Threat landscape: Assess the specific threats your organization faces.
- Compliance requirements: Ensure the solution meets industry regulations.
- Integration with existing tools: Compatibility with your existing security infrastructure.
- Ease of management: Choose a solution that is easy to deploy and manage.
- Cost: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including licensing, implementation, and ongoing maintenance.
How Does Endpoint Security Work?
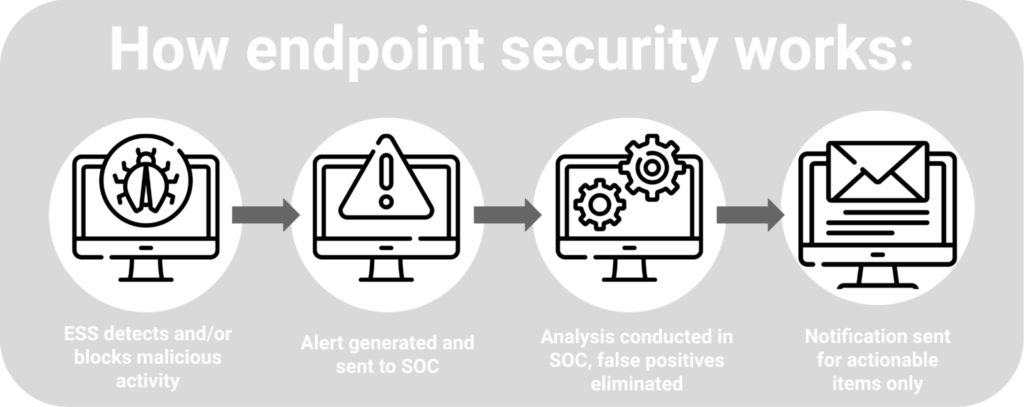
The main goal of any endpoint security solution is to protect data and workflows associated with all devices that connect to the corporate network. It does this by examining files as they enter the network and comparing them against an ever-increasing database of threat information, which is stored in the cloud.
The endpoint security solution provides system admins with a centralized management console that is installed on a network or server and enables them to control the security of all devices connecting to them. Client software is then deployed to each endpoint, either remotely or directly. With the endpoint set up, the software pushes updates to it whenever necessary, authenticates login attempts that are made from it, and administers corporate policies.
In addition, the endpoint security solution secures endpoints through application control. This blocks the user from downloading or accessing applications that are unsafe or unauthorized by the organization. It also uses encryption to prevent data loss.
Endpoint security components
Typically, endpoint security software will include these key components:
- Machine-learning classification to detect zero-day threats in near real time
- Advanced antimalware and antivirus protection to protect, detect, and correct malware across multiple endpoint devices and operating systems
- Proactive web security to ensure safe browsing on the web
- Data classification and data loss prevention to prevent data loss and exfiltration
- Integrated firewall to block hostile network attacks
- Email gateway to block phishing and social engineering attempts targeting your employees
- Actionable threat forensics to allow administrators to quickly isolate infections
- Insider threat protection to safeguard against unintentional and malicious actions
- Centralized endpoint management platform to improve visibility and simplify operations
- Endpoint, email and disk encryption to prevent data exfiltration
What Are the Components of Endpoint Security Software?
A firewall is a network security solution that monitors incoming and outgoing traffic and decides whether to allow or deny access. Endpoint security protects the data on the device itself, enabling the business to monitor the activity and status of all its employees’ devices at all times.
Traditionally, firewalls were ideal for businesses that had all employees working from the same building and signing into the same network. However, with people increasingly working remotely or from home, a firewall no longer suffices as traffic no longer goes through the central network, which leaves devices vulnerable.
This also boils down to businesses protecting networks or endpoints. Network security enables businesses to stop potential security threats at the network level by locking down open ports, restricting traffic, and employing intrusion detection and prevention services. Endpoint security helps businesses keep the devices that connect to a network secure. By making endpoints the new network perimeter, organizations can prevent risks and detect suspicious activity no matter where employees are.
Selecting the right security solution depends on every organization’s individual situation and security requirements. Important factors to build into this decision include:
The number of employees: Small businesses may find a product that requires managing devices on an individual basis works just fine. But as they get larger, it can become more difficult for IT and security teams to manage each device in this manner. Therefore, they will gain huge efficiency by deploying a security solution that centralizes endpoint control.
Employee location: Businesses that have employees working from one central location may not experience any issues with managing endpoint access. But those with a disparate workforce, employees working from home, remote offices, or on the go will need an endpoint security solution that secures endpoints no matter where or when employees attempt to connect to their networks and resources.
Endpoint protection platforms & traditional antivirus
Endpoint protection platforms (EPP) and traditional antivirus solutions differ in some key ways.
- Endpoint Security vs. Network Security: Antivirus programs are designed to safeguard a single endpoint, offering visibility into only that endpoint, in many cases only from that endpoint. Endpoint security software, however, looks at the enterprise network as a whole and can offer visibility of all connected endpoints from a single location.
- Administration: Legacy antivirus solutions relied on the user to manually update the databases or to allow updates at pre-set time. EPPs offer interconnected security that moves administration responsibilities to enterprise IT or cybersecurity team.
- Protection: Traditional antivirus solutions used signature-based detection to find viruses. This meant that if your business was Patient Zero, or if your users hadn’t updated their antivirus program recently, you could still be at risk. By harnessing the cloud, today’s EPP solutions are kept up to date automatically. And with the use of technologies such as behavioral analysis, previously unidentified threats can be uncovered based suspicious behavior.
Types Of Endpoint Security
Endpoint protection platform
Endpoint Protection Platform (EPP) is a comprehensive security solution designed to detect, prevent, and respond to various cyber threats targeting endpoints such as desktops, laptops, mobile devices, and servers. It typically a blanket term for endpoint security solutions that combine multiple security technologies into a single integrated platform, providing capabilities such as antivirus, anti-malware, firewall, intrusion prevention, device control, and data loss prevention.
Anti-virus
Antivirus software is a fundamental component of endpoint security that protects devices from known malicious software such as viruses, worms, Trojans, spyware, and ransomware. It works by scanning files and programs for known signatures and behaviors associated with malware, then quarantining or removing any detected threats.
Endpoint detection and response
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) is a cybersecurity technology that focuses on detecting and investigating suspicious activities and threats on endpoints. Unlike traditional antivirus solutions that primarily rely on signature-based detection, EDR solutions use advanced behavioral analysis, machine learning, and threat intelligence to identify and respond to sophisticated cyber threats that may evade traditional security measures.
Extended detection and response
Extended Detection and Response (XDR) is an evolution of EDR that integrates data from multiple security products and sources across the network, endpoints, cloud, and other environments to provide a more holistic and coordinated approach to threat detection and response.
Internet-of-Things Security
Software that protects Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices is one of the most important types of endpoint security for enterprises. The more IoT devices you have—including ones operated by customers that may interface with your network— the more thorough you have to be when it comes to your security fabric.
Network access control
Network access control (NAC) focuses on managing which users and devices gain access to your network, as well as what they do and which segments they interact with. It uses firewalls that are positioned between users, devices, and sensitive sections of your network.
What Devices Are Classified As Endpoints?
Any device that people interact with while it is connected to your network is classified as an endpoint. The various types of endpoint security software are designed to protect these kinds of devices, including:
- Laptops
- Cell phones
- Tablets
- Printers
- Servers
- Medical devices
- Handheld scanners
- Robots
- All Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices
Endpoint Security Risks & Threats
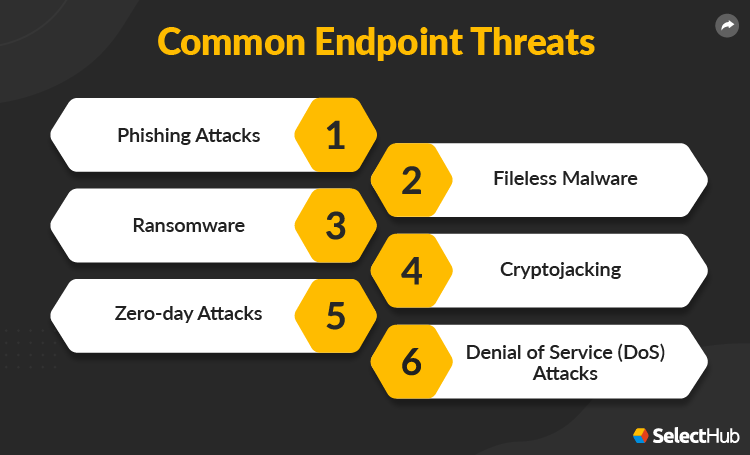
There are many endpoint security risks and threats to defend against, with new threats evolving daily. As noted above, zero-day attacks are among the most common reported when it comes to endpoint incursions. While insider threats are a concern, the largest threat to businesses today comes from external criminal activity.
Endpoint Threats
Here are some of the most common endpoint threats today:
- Phishing. Phishing attacks involve individuals (or bots) posing as legitimate parties in an attempt to gain access to sensitive data. This can occur over email, phone, text, or chat. Security awareness training alongside technical solutions like screening phishing IP addresses and sandboxing inbound email addresses can help to prevent or limit the impact of phishing.
- Ransomware. Ransomware blocks access to a device or files until the attacker gets what they demand (often money or data). Anti-malware and antivirus solutions are your best defense.
- Device Vulnerabilities. Unpatched vulnerabilities in devices and software provide access points for attackers. Be sure that all of your systems, hardware and software are up-to-date and running the most recent versions.
Dealing with User Error
No matter how great your security measures are, they can’t stop your employees from volunteering sensitive data to a phishing scam, typing in a password on a public Wi-Fi network, or otherwise opening the door to an attack through ignorance or carelessness. Be sure to provide comprehensive security training so that you employees are aware of the most common threats and understand your policies.
What is the Difference Between Endpoint Security and a Firewall?
A firewall is a network security solution that monitors incoming and outgoing traffic and decides whether to allow or deny access. Endpoint security protects the data on the device itself, enabling the business to monitor the activity and status of all its employees’ devices at all times.
- The number of employees: Small businesses may find a product that requires managing devices on an individual basis works just fine. But as they get larger, it can become more difficult for IT and security teams to manage each device in this manner. Therefore, they will gain huge efficiency by deploying a security solution that centralizes endpoint control.
- Employee location: Businesses that have employees working from one central location may not experience any issues with managing endpoint access. But those with a disparate workforce, employees working from home, remote offices, or on the go will need an endpoint security solution that secures endpoints no matter where or when employees attempt to connect to their networks and resources.
- Device ownership: The rise of BYOD has blurred the lines of device ownership. Employees increasingly use their own devices to sign in and out of business networks and need to do so securely. An endpoint security solution enables businesses to secure employees every time they sign in to their networks and monitor access at all times.
- Data sensitivity: Businesses that handle high-value intellectual property or sensitive data will find that antivirus software does not suffice in safeguarding their data, as it only protects it from viruses. To protect themselves from data loss incidents that pose a huge financial and reputational risk, these organizations need to deploy endpoint security solutions. Doing so will help them protect their most critical data, meet compliance requirements, and pass their audits.
Network Security Difference B/w Endpoint Security
It’s important to differentiate between network security and endpoint security, as the two are often confused. Network security focuses on hardware and software designed to protect your data and the integrity of the system housing it, typically by managing access to the network. Often, this can extend to on-site computers, but it may disregard other devices accessing the network, especially remotely.
Best Practices
Regularly Monitor and Update Endpoints
Monitor your network and endpoints to identify abnormal activities or potential breaches. Keep all systems and tools updated with the latest patches to prevent attackers from exploiting known vulnerabilities.
Implement Endpoint Encryption
Encrypt all information stored on endpoints to protect data confidentiality and integrity, particularly when devices might be lost, stolen or accessed by unauthorized individuals.
Apply Zero-Trust Security Measures
Adopt a zero-trust approach to continuously verify every user and device trying to access the network or resources, regardless of location. This model grants users access only to specific resources they need to perform their tasks.
Establish Strong Passwords and Access Control
You can encourage or enforce the use of strong, unique passwords and implement multi-factor authentication wherever possible. Develop strict policies for remote access, ensuring secure connectivity for remote employees.
Conduct Employee Training
Invest in security awareness training programs for your employees. Most cyberattacks originate from human error, so keep your team informed about the latest threats and prevention strategies.
Develop an Incident Response Plan
Have a clear plan for responding to security incidents. It should outline the steps you must take following breach identification, including isolating affected systems, investigating the breach, notifying relevant parties and implementing preventive measures to avoid future incidents.

Endpoint Security Policy
A comprehensive endpoint security policy is essential to help ensure all of your devices and vulnerabilities are protected.
In addition to utilizing endpoint software and services, you need to create clear guidelines for security standards and train employees so they understand the risks, their responsibilities and the penalties for failing to comply. You may have to put an end to “bring your own device” options that put your network at risk, even if it costs you more to provide secured devices.
CDW Cybersecurity Experts Can Help
You don’t want to wait until an endpoint attack occurs to change your systems and procedures. Implementing security measures now, including strict policies and procedures to go with your software and services, can save you from an attack that could significantly impact your business, customers and ability to maintain operations.
From designing your endpoint security plan and recommending the best solutions for your needs to active management and incident response, CDW cybersecurity experts are ready to assist you. Contact us to learn more about our solutions and services.
Conclusion
Endpoint security is a critical component of any comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. As the gateway between an organization’s network and the external world, endpoints (such as laptops, desktops, and mobile devices) are prime targets for cyberattacks.
Key Takeaways
- Endpoint security is essential: Given the increasing complexity and sophistication of cyber threats, protecting endpoints has become more crucial than ever.
- A layered approach is necessary: Effective endpoint security requires a combination of technologies, including antivirus software, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions.
- Employee education is vital: Users play a crucial role in preventing security breaches. Training employees on best practices, such as strong password creation, phishing awareness, and secure browsing habits, is essential.
- Continuous monitoring and adaptation: The threat landscape is constantly evolving. Therefore, regular security assessments and updates to endpoint protection measures are necessary.
- The rise of remote work: With the increasing number of remote workers, endpoint security has become even more challenging. Organizations must implement robust security measures to protect endpoints outside the corporate network.
In conclusion, by prioritizing endpoint security, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage. A proactive and layered approach to endpoint protection is essential to safeguard sensitive information and maintain business continuity.
FAQs
An endpoint is any device that employees use to connect to business networks represents a potential risk that cyber criminals can exploit to steal corporate data.
Endpoint security is the process of protecting devices like desktops, laptops, mobile phones, and tablets from malicious threats and cyberattacks.
Antivirus software helps businesses detect, eliminate, and prevent malware from infecting devices. Antivirus solutions are installed directly on endpoint devices, such as laptops, PCs, network servers, and mobile devices. Endpoint security solutions protect the entire business network instead of protecting an individual device.